1. Selection of fastener surface treatment process
The choice of surface treatment is a problem that every designer faces. There are many types of surface treatments to choose from, but the principle is only one "economical and practical".
Since almost all commercial fasteners are made of carbon steel and alloy steel, general fasteners are expected to prevent corrosion. In addition, the surface treated coating must be firmly attached and cannot be peeled off during installation and removal. For threaded fasteners, the coating must be thin enough to allow the plated threads to still be threaded. Generally, the temperature limit of the coating is lower than that of the fastener material, so it is also necessary to consider the operating temperature requirements of the fastener.
For surface treatment, people generally pay attention to aesthetics and anti-corrosion, but the main function of the fastener is to fasten the parts, and the surface treatment has a great influence on the fastening performance of the fasteners. Therefore, when selecting the surface treatment, The factor of fastening performance should also be considered, namely the mounting torque - the consistency of the preload.
A high-level designer should not only consider the design, but also pay attention to the technicality of the assembly and even the environmental requirements.
In the following, according to the above factors, some commonly used coatings for fasteners are briefly introduced for reference by fastener practitioners.
Electroplated zinc
Electrogalvanizing is the most common coating for commercial fasteners. It is cheaper and looks better. It can be black or military green. However, its anticorrosive properties are general, and its anticorrosive properties are the lowest among the zinc plating (coating) layers. Generally, the electroplating zinc neutral salt spray test is carried out within 72 hours, and a special sealing agent is also used, so that the neutral salt spray test is more than 200 hours, but the price is expensive, which is 5-8 times that of general galvanizing.
Electroplating process is easy to produce hydrogen embrittlement, so bolts above 10.9 are generally not treated with galvanizing. Although the oven can be used to remove hydrogen after plating, the passivation film will be destroyed at 60 °C or above, so dehydrogenation must be It is carried out before passivation after electroplating. Such operability is poor and processing costs are high. In reality, general manufacturers do not take the initiative to dehydrogenate unless mandatory by specific customers.
The electro-galvanized fastener torque—preload force consistency is poor and unstable, and is generally not used for connection of important parts. In order to improve the torque-pre-tightness consistency, it is also possible to improve and improve the torque-preload consistency by applying a lubricant after plating.

Phosphating
A basic principle is that phosphating is cheaper than galvanizing and its corrosion resistance is worse than galvanizing. After phosphating, oil should be applied, and its corrosion resistance has a great relationship with the performance of the oil. For example, after phosphating, the general anti-rust oil is applied, and the neutral salt spray test is only 10 to 20 hours. Apply high-grade anti-rust oil for 72 to 96 hours. However, its price is 2 to 3 times that of ordinary phosphating oil.
Two types of fastener phosphating are commonly used, zinc phosphating and manganese phosphating. Zinc phosphating lubrication performance is better than manganese phosphating, manganese phosphating corrosion resistance, wear resistance is better than galvanizing. It can be used at temperatures ranging from 225 to 400 degrees Fahrenheit (107 to 204 ° C).
Especially the connection of some important parts. For example, engine connecting rod bolts, nuts, cylinder heads, main bearings, flywheel bolts, wheel bolt nuts, etc.
High-strength bolts are phosphated to avoid hydrogen embrittlement problems. Therefore, bolts of grade 10.9 or higher in the industrial field are generally treated with a phosphating surface.
Oxidation (blackening)
Blackening + oiling is a popular coating for industrial fasteners because it is the cheapest and looks good before the oil is exhausted. Since blackening has almost no rust-preventing ability, it will rust quickly without oil. In the oily state, the neutral salt spray test can only reach 3 to 5 hours.

Cadmium plating
The cadmium coating has good corrosion resistance, especially in the marine atmosphere, and the corrosion resistance is better than other surface treatments. The waste liquid treatment in the process of electroplating cadmium is expensive and costly, and its price is about 15-20 times that of electrogalvanized. Therefore, it is not used in the general industry and is only used in certain specific environments. For example, fasteners for oil rigs and Hainan aircraft.
Chrome plating
The chrome plating layer is stable in the atmosphere, is not easy to change color and lose luster, and has high hardness and good wear resistance. The use of chrome plating on fasteners is generally used as a decorative effect. It is rarely used in industrial applications where high corrosion resistance is required, because good chrome plated fasteners are as expensive as stainless steel, except when stainless steel is not strong enough to be replaced with chrome-plated fasteners.
To prevent corrosion, copper and nickel should be plated first before chrome plating. The chrome plating can withstand temperatures up to 1200 degrees Fahrenheit (650 ° C). However, hydrogen embrittlement is also present in the same way as electrogalvanizing.
Nickel plating
It is mainly used in places where both corrosion protection and conductivity are required. Such as the terminal of the vehicle battery, etc.
Hot dip zinc
Hot dip zinc is a thermal diffusion coating that is heated to a liquid under zinc. The coating thickness is 15~100μm, and it is not easy to control, but it has good corrosion resistance and is used in engineering. The hot dip zinc processing process is seriously polluted, such as zinc scrap and zinc vapor.
Due to the thick plating layer, the problem that the inner and outer threads are difficult to be screwed is caused in the fastener.
Due to the temperature of hot dip galvanizing, (340-500C) it cannot be used for fasteners above 10.9.
Zinc infiltration
Zinc infiltration is a solid metallurgical thermal diffusion coating of zinc powder. The uniformity is good, and a uniform layer can be obtained in the thread and the blind hole. The coating thickness is 10~110μm, and the error can be controlled at 10%. Its bond strength and corrosion resistance to the substrate are best in zinc coatings (galvanized, hot dip galvanized, dacromet). Its processing process is non-polluting and the most environmentally friendly.
DacroThere is no hydrogen embrittlement problem, and the torque-preload force is consistent. If you don't consider the environmental protection of hexavalent chromium, it is actually the most suitable for high-strength fasteners with high corrosion resistance.

Introduction to Common Processes for Surface Treatment of Fasteners---Electroplating1. Pre-plating treatment classification
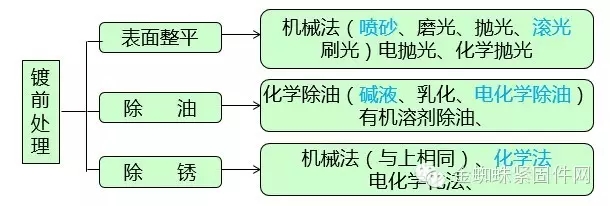
Electrochemical degreasing: also called electric de-oiling, placing the part on the cathode or anode, passing the direct current under the action of current, the surface tension of the interface between the oil and the solution is greatly reduced, and the generated oxygen on the surface is attached. Has a strong tearing effect.
Electrochemical degreasing according to the workpiece is divided into cathode method and anode method, and cathode-anode combination method. The efficiency of degassing is higher than that of anode method. The substrate is not corroded, but it is easy to permeate hydrogen. It is suitable for aluminum zinc, tin, lead, copper, etc. Non-ferrous metals and alloy parts are degreased. The anode degreasing efficiency is lower than that of the cathode. It is highly corrosive to non-ferrous metals and is suitable for high carbon steel and elastic material parts.
Chemical derusting: chemical derusting mostly uses acidic solution, so it is also called pickling, also known as erosion, strong erosion, weak erosion (activation)
2. Pre-plating process

3. Introduction to galvanizing process
Process characteristics of potassium chloride galvanizing:
Potassium chloride galvanizing is suitable for the barrel plating of fasteners due to its wide plating resistance and high current efficiency. In addition, potassium chloride galvanizing allows for a wide current density, and the plating solution is stable, contains no complex, and the wastewater treatment is simple. Therefore, most manufacturers use the potassium chloride galvanizing process.
4. Operating points
1) Control of the loading and current of the parts:
The size and length of the products vary, and the difference is large. In order to facilitate the operation and adapt to the process requirements, the product loading is specified. The products of various specifications are 30 cm above, the lower circle is 25 cm, and the height is 25 cm. Shaped buckets filled with 4 barrels for one plating tank (ie 3 drums). Based on this amount, the total surface area of ​​each part is calculated, and then multiplied by the current density required by the process to determine the current range of the galvanization of the parts. The current control of each specification product is detailed in the attached table for reference.
Reference accessories: standard parts galvanizing current comparison table
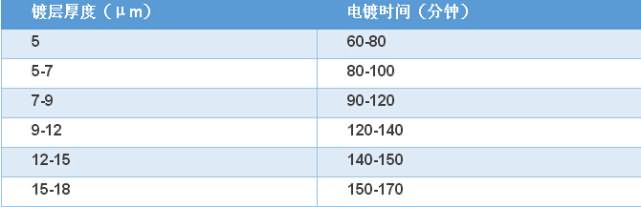
2) Control of plating thickness and plating timeWhen the load and current of the product are controlled to a certain value, the thickness of the coating depends only on the length of the plating time. The longer the time, the thicker the coating. The plating thickness requirements and time control are as follows:
3) Adding brightenerIn order to obtain a bright coating, brighteners and softeners are added to each shift. When added, it was diluted with 5-10 times of water. If the brightener is added too little, the bright and ideal coating will not be obtained. If it is added too much, it will cause the coating to be brittle and loose, and even the organic impurities will be precipitated due to excessive light, which will be attached to the coating, resulting in blistering and peeling of the coating. . The amount of brightener added is proportional to the energization time and current, and is added in an appropriate amount within a range of consumption of 60-120 ml/KAh. Each shift is calculated in 4 hours: 200 ml of softener and 1000 ml of brightener.
5. Maintenance of plating solution
a) The potassium chloride plating solution is relatively stable. The bath liquid components are tested once a week in a single shift production, and the two shifts are analyzed once every three days, and the necessary supplements are made according to the analysis results. And do a good job in the plating process inspection record.
b) The pH value of the plating solution is measured once per shift. The pH rise can be adjusted to 5-6 with dilute hydrochloric acid, and the zinc plate consumption is checked and replenished in time.
c) The metal at the bottom of the tank should be sucked out before work every day to prevent the metal from being dissolved in the solution to affect its performance and the quality of the coating.
d) Regularly carry out large-scale treatment, generally prescribed for 1-2 months, and make a record of plating process inspection.
6. Introduction to the process after plating (zinc)
In the pickling, cathodic de-oiling and electroplating processes, the parts may permeate hydrogen in the crystal lattice of the plating layer and the base metal, causing the lattice to be distorted, the internal stress to increase, and the brittleness to be called hydrogen embrittlement.
Hydrogen removal
In order to eliminate hydrogen embrittlement, post-plating heat treatment is generally used to allow hydrogen to escape. The higher the temperature, the longer the time, the more complete the removal of hydrogen, but the crystal structure of zinc will be deformed, brittle and the corrosion resistance will decrease significantly when it exceeds 250 °C. Practice temperature: 200±10 °C, the hydrogen removal process of different standard parts products is shown in the following table:
Part Name
*Note: It is carried out within four hours after plating, and the furnace temperature is uniform.Passivation treatment
a. Zinc is active in nature and easily oxidizes and darkens in the air, producing "white rust" corrosion. After chromate treatment with chromate, a chemical conversion film can be formed on the zinc layer to make the active metal zinc in a passive state. This layer of chromic acid film with a thickness less than 0.5 UM can make the corrosion resistance of the galvanized layer. Improve 6-8 to accompany. And give a beautiful decorative appearance and anti-pollution ability.
b. The depth of passivation solution is divided into three types: high, medium and low. In order to meet the requirements of different customers, the color of blunt flowers is divided into blue, multicolored, black, military green, golden yellow, trivalent blue and trivalent multicolored.
Three elements of chromic acid purified salt
Although there are many passivation formulas, any practical formula must include a main salt, an activator, and a certain hydrogen ion concentration.
Precautions
(1) The quality of the coating is required to be fine and the gloss is good. Since the low concentration passivation solution has no chemical polishing ability, the quality of the zinc plating layer must be kept consistent.
(2) The passivation temperature is preferably 15 ° C to 35 ° C. The temperature is low, the film formation is slow, the color film is thin, the temperature is high, the film thickness is loose and the adhesion is not strong. Automatic line production is best controlled at around 25 ° C to ensure the same color is obtained within a certain period of time.
Passivation time
It depends on the concentration of the main salt, the pH, the concentration of the activator and the temperature. In particular, the automatic line must keep the above factors within the scope of the specification. When the other conditions are the same, the summer passivation time is shortened accordingly; in winter, it is appropriately extended.
(1) The relative movement of the part and the passivation liquid during passivation is beneficial to the convection diffusion of the solution, preventing the parts from sticking and making the film layer uniform. Automatic line passivation must be stirred vigorously with compressed air.
(2) The cleaning must be thorough, the temperature of the hot water should not exceed 50 °C, otherwise it will easily fall off the film.
(3) Color passivation must be baked and aged to improve the adhesion and corrosion resistance of the film. However, the aging temperature must not exceed 65 °C. When the temperature is high, the film dewaters and cracks, and the corrosion resistance is significantly reduced. In addition to paying attention to temperature when using infrared drying, the aging time should not exceed 15 minutes, otherwise the corrosion resistance will also decrease.
Related information recommended:
Selection and Introduction of Surface Treatment Process for Fasteners (II) - Phosphating / Oxidation
The stainless steel architecutural net is made of stainless steel materail to avoid rust and corrode. This kind of wire mesh is expensive than other metal wire mesh, but it can last longer years and have beautifull sufface, So the stailess steel mesh net is widly used in follow area building facade. cable mesh for railing, balustrade, staircase. handrail. balcony infill. wire rope mesh fence. leight weight flexible green wall. Safety Net on bridge. bird netting, aviary mesh. monkey enclosure mesh. tiger enclosure mesh. zoo mesh. animal enclosure mesh.
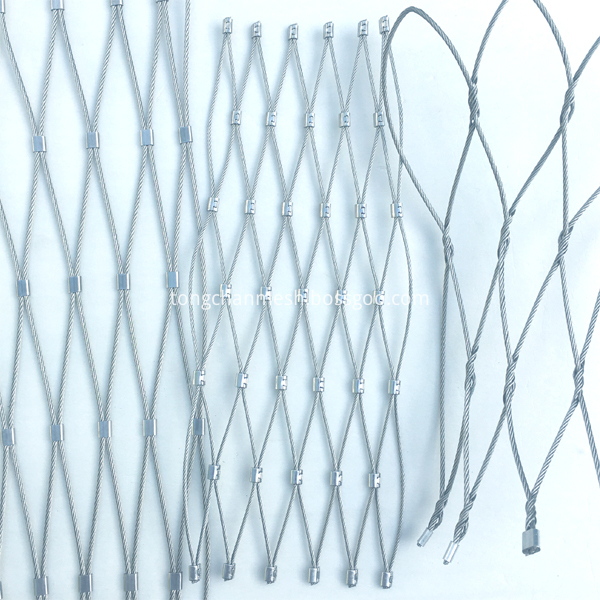


Stainless Steel Architectural Net
Stainless Steel Architectural Net,Architectural Mesh,Architectural Net,Architectural Flexible Stainless Steel Net
Hebei TongChan Imp.&Exp.Co., Ltd. , https://www.tongchanmesh.com