Abstract The performance of machine tools greatly affects the competitiveness of products and has a huge impact on the overall industrial strength of the country. Therefore, the machine tool industry is regarded as a basic equipment industry by all countries and has made great contributions to industrial development. Japanese machine tools are based on their high quality and excellent reliability...
The performance of the machine tool greatly affects the competitiveness of the product and has a huge impact on the overall industrial strength of the country in which it is located. Therefore, the machine tool industry is regarded as a basic equipment industry by all countries and has made great contributions to industrial development. Japanese machine tools have earned an enviable reputation worldwide for their high quality and excellent reliability. From the perspective of Japan, the world machine tool market is still in a recession. However, in September 2016, the International Manufacturing Technology Exhibition (IMTS) in Chicago, USA, showed a busy scene. Despite the weak investment in equipment during this period, the number of visitors to IMTS reached a record high.
According to the Japan Machine Tool Manufacturers Association (JMTBA), since the total amount of sales orders for Japanese machine tools reached a peak of 1.5093 trillion yen in 2014, the order value of machine tools has continued to decline in the past two years. The machine tool industry is a cyclical industry (as shown in Figure 1), for example, it repeats every three years. Once the industry has completely fallen to the bottom, it will eventually rise.
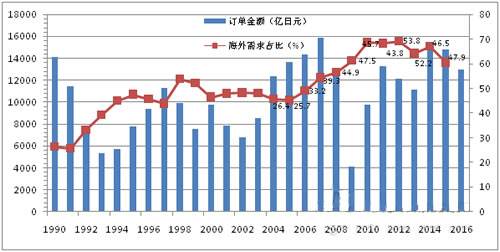
Figure 1 Trends in Japanese machine tool sales orders over the years (2016 is forecast, data source: JMTBA)
There is a regular event in the Japanese machine tool industry. Every January, the chairman of the Japan Machine Tool Manufacturers Association (JMTBA) announces the target sales for the year at the New Year celebrations. President Hanaki Yoshimaro announced that this year's target sales of 1.550 trillion yen, which is the second largest goal in the history of the association, surprised participants, because this goal will be difficult to achieve. The target sales of last year (2015) was also 1.550 trillion yen. Sales in the first half of last year showed an upward trend, but the trend in the middle of the year was reversed. The final sales in 2015 was 1.4805 trillion yen. This number is the second highest level in the history of the Association, but it is also the first decline in the past two years. The machine tool market has entered a recession phase. In 2016, this trend continued, mainly due to the end of the special needs of smartphone parts for machine tools, such as the metal frame of Apple's “iPhoneâ€, which led to strong sales growth in 2014. The continued surge in demand from US investment companies has slowed and the Chinese economy has slowed, which has led to the stagnation of the Southeast Asian market. In Japan, the weak yen has benefited equipment investors, but after the UK exited the EU, the yen is on the rise, but figures show that investment is stagnating. Based on these circumstances, JMTBA revised the forecast sales of 1.50 trillion yen to 1.30 trillion yen.
Still, it is not time to be pessimistic. If annual sales reach 1.300 trillion yen, then monthly sales will exceed the strong sales threshold of 100 billion yen. This level is still good. In Japan and the United States, the sales of machine tools used to manufacture aircraft parts are strong. The market (machine tools for aircraft parts) is still small, but it is still undoubtedly growing. Based on the cyclical trend of the industry, sales in 2018 may show a cyclical growth trend. Especially when the world economy is in chaos, it is important to actively consider equipment investment and prepare for it.
Throughout history, the progress of the Japanese machine tool industry has been remarkable. In particular, Japanese machine tool manufacturers have shown great interest in the application of CNC technology. In the early 1950s, the United States developed this technology. Due to the introduction of this technology in Japan, Japan has quickly realized the further development of this technology. As of the 1970s, the world market has begun to appreciate the performance of Japanese CNC machine tools. Due to the growing wave of mainstream CNC machine tools, Japan became a world leader in the production of CNC machine tools in 1982, although the market was still dominated by the US. After that, Japan maintained its leading position in the machine tool field, resisting the impact and distortion of history, including the end of the Cold War between East and West, the collapse of the Japanese economic bubble and the restructuring of the global automotive industry. Following the trend of continued globalization of the world economy, Japan has fulfilled its responsibilities and provided high-performance machine tools for the world's manufacturing industry.
Since 2003, the value of Japanese machine tool production has risen again, mainly due to the surge in demand from China and other emerging markets. In 2007, the output value reached 1.30 trillion yen for the first time in the past 17 years, and the industry has shown a boom.
However, by September 2008, it was hit by the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers. This has caused a serious blow to the world and has had a serious impact on the business of the Japanese machine tool industry. Although the business was still active in early 2008, the growth rate has slowed down. In 2009, the output value suddenly dropped to 486.3 billion yen. This is a trough in the past 30 years.
The recovery began in 2010, mainly due to the substantial increase in foreign demand. In 2011, it suffered an unprecedented disaster. In March, Japan was hit by a major earthquake. It has seriously disrupted Japan’s economic activity channels, including power shortages. Despite this, in 2011, the output value reached 1 trillion yen for the first time in the past three years. Since then, the output value has stagnated at around 1 trillion yen for five consecutive years.
In terms of trade, in the post-war period, the import volume greatly exceeded the export value, mainly because the domestic machine tools did not have sufficient supply channels and technical capabilities. However, since the 1960s, when domestic machine tools showed a competitive advantage, the export volume increased significantly. In the end, exports in 1972 exceeded imports. Since then, despite occasional stagnation, exports have continued to grow, mainly driven by the strong international competitiveness of Japanese CNC machine tools. At the same time, imports continued to be below 100 billion yen, except in 2005 and 2006. However, since 2009, the import volume has increased for six consecutive years, which means that the import demand for special equipment continues to grow.
Since 1963, JMTBA has voluntarily compiled statistics for its members, which is known as the Machine Tool Order Survey.
In 2015, the total order value of Japanese machine tools reached 1.4806 trillion yen (see Figure 2), down 1.9% year-on-year. This shows the first decline in two years. However, the total order amount has reached 1 trillion yen for five consecutive years, which is the third highest in the past.
In terms of domestic demand, domestic orders in Japan increased to 586.2 billion yen, an increase of 18.1% year-on-year. This shows continued growth for three consecutive years. The growth in corporate profits further weakened the yen due to the growth in alternative demand. In addition, it has been influenced by various government policies, such as productivity improvement taxation, manufacturing subsidies, and other policies that encourage domestic demand. This is also the case after the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers (2008), the order volume reached 500 billion yen for the first time. In terms of industries, in 2015, general machinery orders reached 221.8 billion yen, an increase of 10.9%; the automotive industry reached 203.9 billion yen, an increase of 21.6%; the precision instrument industry reached 21.1 billion yen, an increase 23.2%; the aircraft, shipbuilding and transportation equipment industry reached 31.2 billion yen, an increase of 51.5%. However, the electrical machinery industry fell by 1.7% to 26.9 billion yen; public institutions and schools reached 3.4 billion yen, down 17.6%.

Figure 2 Orders of Japanese machine tools over the years (amount of units: 100 million yen)
In terms of external demand, in 2015, the number of overseas orders in Japan was 894.4 billion yen, a year-on-year decrease of 11.7%. This shows the first decline in two years. However, this number ranks third in past history. The order amount is still maintained at a high level. Among them, Asia fell to 443.5 billion yen, down 14.5% year-on-year, indicating the first decline in two years, mainly due to the impact of China's economic recession. Orders in Europe were 181 billion yen, down 4.5%, the first decline, mainly due to the recurrence of the Greek debt crisis, Volkswagen issues and frequent terrorist attacks. Orders in North America fell by 10.4% to 566.2 billion yen, the first decline in six years. This figure reflects the impact of the energy industry, mainly due to the weakness of the crude oil industry, China's economic recession and the dollar's strong export sluggishness. Nevertheless, the automotive and aircraft products industries are still strong. According to the production statistics reported by the Industrial Production Survey published by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) (see Figure 3), in 2015, the output value of Japanese machine tools reached 1.2581 trillion yen, an increase of 6.1% over the previous year. It has reached 1 trillion yen for two consecutive years. The output value of CNC machine tools reached 1.1415 trillion yen, an increase of 6.5% over the previous year. The proportion of CNC products accounted for 90.7%, an increase of 0.3 percentage points over the previous year. In the past year, 5 of the 6 categories showed an increasing trend, so gear and finishing machines increased by 35.4%, grinding machines increased by 13.3%, lathes increased by 11.2%, and machining centers increased by 6.4%. Other machine tools The increase was 3.1%, and the dedicated machine tool dropped by 16.7%.
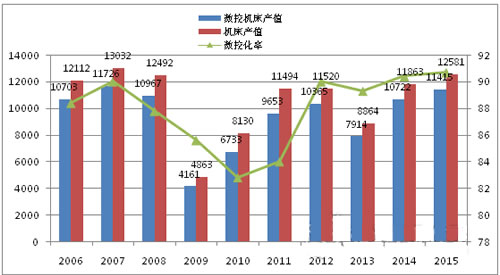
Figure 3 Statistics of Japanese machine tool output over the years (amount of units: 100 million yen Source: METI)
According to the proportion of total output value, in 2015, the total output value of the machining center accounted for 42.2% of the total output value of the machine tool; followed by lathes accounted for 24.6%; other machine tools accounted for 14.3%; grinding machines accounted for 9.6%; special machine tools accounted for 7.1%; gear cutting and Grinding machine tools accounted for 2.2%. According to the "2015 World Machine Tool Production and Consumption Survey" published by Gardner Publishing Company in April 2016, China's machine tool production value has ranked first in the world for seven consecutive years, Japan ranked second for two consecutive years, and Germany ranked third. Bit.
According to trade statistics compiled by the Japanese Ministry of Finance (MOF) (see Figure 4), in 2015, Japanese machine tool exports reached 932.1 billion yen, down 3.1% from the previous year. In this figure, the export value of CNC machine tools reached 884.4 billion yen, down 2.7% from the previous year, and the proportion of CNC machine tools accounted for 94.9%.
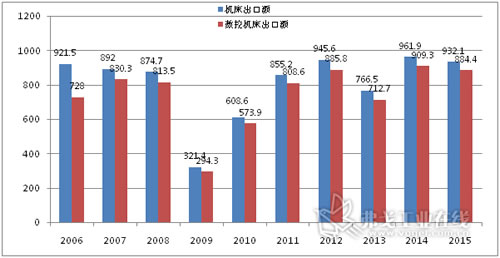
Figure 4 Statistics of Japanese machine tool exports over the years (amount of units: 1 billion yen Source: MOF)
According to the export value of machine tools by destination, Japan’s exports to East Asia reached 357.7 billion yen in 2015, down 6.9% from the previous year, including South Korea and Taiwan. The export value of other Asian markets reached 2006 billion yen, an increase of 0.5% over the previous year, including Thailand and India. The export value of the Asian market reached 558.3 ​​billion yen, down 4.3% from the previous year. The export value of the European market reached 134.9 billion yuan, an increase of 8.2% over the previous year. The South American market's exports reached 215.6 billion yen, down 7.9% from the previous year. Among the share of exports, Asia accounted for 60.0%, North America accounted for 23.1%, and Europe accounted for 15.0%. According to the types of export products of machine tools, machining centers account for 50.1%, and lathes account for 22.6%, so the proportion of these two categories exceeds 70%. Other categories: 10.6% for special machine tools and 9.7% for grinding and grinding machines.
Looking at the figures, Japan’s export ratio (exports/output value × 100%) accounted for 74.1%, and the proportion of exports increased due to the increase in overseas orders (60.4%). It should be noted that the survey of industrial production statistics of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan only covers companies with more than 50 employees. The overseas trade statistics (exports) issued by the Ministry of Finance cover not only new machine tools, but also second-hand machine tools.
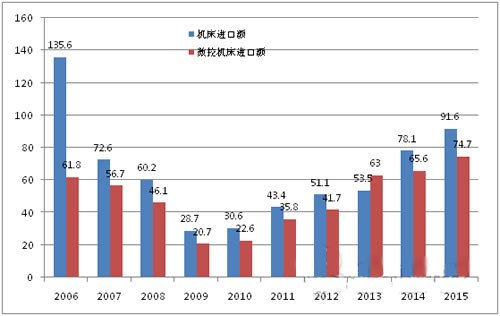
Figure 5 Statistics of Japanese machine tool imports over the years (amount of units: 1 billion yen Source: MOF)
In 2015, Japanese machine tool imports reached 91.6 billion yen, an increase of 17.3% over the previous year (see Figure 5). This shows that there has been a growth trend for six consecutive years. Among them, the import value of CNC machine tools reached 74.7 billion yen, an increase of 14.0% over the previous year. The proportion of CNC machine tools accounted for 82.0%, down 2.0 percentage points from the previous year. The main source of imports is Germany, with an import value of 23.7 billion yen, an increase of 30.8% over the previous year. China's 18.8 billion yen, an increase of 5.8% over the previous year; Switzerland accounted for 10.9 billion yen, an increase of 39.0% over the previous year; Taiwan, China 9.5 billion yen, an increase of 16.1% over the previous year; Thailand 8.6 billion The yen was up 3.4% from the previous year; the US was 6.3 billion yen, down 7.9% from the previous year; South Korea was 3.8 billion yen, up 1.7% from the previous year. This figure shows that Japanese local machine tool manufacturers' imports from Asia are on the rise. In 2015, the top seven sources of imports accounted for 90% of the total machine tool import sources. According to the types of imported products: special machine tools (laser beam machine tools and EDM machines) accounted for 33.4%, lathes accounted for 25.7%, machining centers accounted for 10.9%, and grinding and grinding machines accounted for 16.5%. Ceramic Nozzle,Alumina Nozzle,Tig Ceramic Nozzle,Alumina Ceramic Nozzle
Shaodong Lida Tools Co.,Ltd , https://www.hailiweld.com