 China has to gradually realize the transition from a mold manufacturing country to a mold manufacturing powerhouse. This consensus has been in place for a long time. Jin Monet CEO Luo Baihui believes that equipment manufacturing industry is the "engine" and "heart" of China's industry and national economy. Equipment manufacturing industry, especially major technical equipment, is a concrete embodiment of a country's overall national strength. It is an inevitable trend to revitalize the equipment manufacturing industry and promote the internationalization of the equipment manufacturing industry.
China has to gradually realize the transition from a mold manufacturing country to a mold manufacturing powerhouse. This consensus has been in place for a long time. Jin Monet CEO Luo Baihui believes that equipment manufacturing industry is the "engine" and "heart" of China's industry and national economy. Equipment manufacturing industry, especially major technical equipment, is a concrete embodiment of a country's overall national strength. It is an inevitable trend to revitalize the equipment manufacturing industry and promote the internationalization of the equipment manufacturing industry. 2013 is a crucial year for China to thoroughly implement the industrial transformation and upgrading plan and strategic emerging industry development plan. High-end equipment manufacturing industry will usher in an important period of development opportunities. China's equipment manufacturing industry will face the coexistence of both opportunities and challenges. This is because after entering 2013, although China will continue to invest more in large-scale infrastructure construction such as high-speed rail and urban rail transit to boost domestic demand, these are all The period from tendering to procurement and construction is relatively slow, and for the equipment manufacturing industry in which China has experienced a declining growth rate, the promotion role in the short term is limited.
Whether it is from the perspective of appreciation of renminbi or from the perspective of Chinese companies’ cash flow accumulation in recent years and the formation of internationalized acquisition capabilities, it is now a good time for Chinese companies to promote overseas mergers and acquisitions. The equipment manufacturing companies must have a certain "wolf spirit" when doing overseas mergers and acquisitions. They do not have to be defensive and can take the initiative to attack. The lawsuit must be played. At the same time, we also need to do a good job in the early stage and prudently promote our internationalization strategy.
Under the encouragement and support of the national policy, all parts of the country are making great efforts to promote the transformation and upgrade of the mold equipment manufacturing industry. The Chinese economy has developed into an important transition period, and the mould equipment manufacturing industry is one of the most crucial pawns in the national strategic transformation. The investment prospects of China's mold equipment manufacturing industry are very broad.
According to media reports, in the face of global economic adjustment opportunities, Shandong has intensified the implementation of high-end, high-quality, and high-efficiency industry development strategies, and through the intensification of technological transformation, it has achieved breakthrough development in the high-end manufacturing industry and boosted the equipment manufacturing industry from big changes. In 2012, Shandong's mold and equipment manufacturing industry invested hundreds of billions of yuan in technological transformation, accounting for more than 30% of industrial technology investment. Thanks to the increase in investment in technological transformation of molds and the breakthrough in high-end industries, the development of the equipment industry in the province has steadily increased since the fourth quarter.
It is reported that in the next five years, Xiangyang equipment manufacturing industry will be based on the needs of the national manufacturing industry to upgrade and develop, and will vigorously develop high-end equipment and supporting industries with outstanding innovation, high added value, and broad market application prospects. Accelerate the development of high-end equipment manufacturing industry clusters represented by aerospace equipment, smart manufacturing equipment, and rail transit equipment, and continue to expand the general equipment manufacturing industry for metal products, castings and forgings, molds, and bearings, and actively nurture and develop electrical equipment and engineering machinery. Environmental protection equipment, emergency rescue equipment, and remanufacturing and other characteristic equipment manufacturing industries form the “1358†industry development priority and provide strong support for building “industry Yingyangâ€. In this regard, Luo Baihui analysis said that China's mold equipment manufacturing industry in the future to replace the obvious trend. Judging from past industry experience, the low-end areas of China's mold equipment manufacturing industry have basically achieved localization. Domestic-funded enterprises in the mid-to-high-end sector are gradually replacing their imports by virtue of their comparative advantages in cost, channels, and services, and are expected to go abroad to join. To the international market competition.
Luo Baihui believes that only companies with differentiated competitive advantages in terms of cost, technology, sales channels, and services can gain a dominant position in the fierce market competition in the future. In the selection of specific investment targets, attention should be paid to safety margins and emerging high-end manufacturing fields with high growth potential.
Product List
|
aluminium trihydrate (ATH) |
21645-51-2 |
|
magnesium hydroxide (MDH) |
1309-42-8 |
|
antimony trioxide (ATO) |
1309-64-4 |
|
Zinc borate |
1332-07-6 |
|
Melamine polyphosphate (MPP) |
218768-84-4 |
|
Melamine phosphate (MP) |
20208-95-1 |
|
Melamine Cyanurate(MCA) |
37640-57-6 |
|
68333-79-9 |
Introduction
The most common inorganic flame retardants are the hydroxides or aluminium and magnesium. Aluminium trihydroxide (ATH) is by far the most widely used Flame Retardant on a tonnage basis. It is inexpensive, but usually requires higher loadings in polymers of up to more than 60%, because the flame retardant mechanism is based on the release of water which cools and dilutes the flame zone. Magnesium hydroxide (MDH) is used in polymers which have higher processing temperatures, because it is stable up to temperatures of around 300 C versus ATH which decomposes around 200 C.

Fine precipitated ATH and MDH (grain size < 2um) are used in melt compounding and extrusion of thermoplastics like cable PVC or polyolefins for cables. For use in cable, ATH and more often MDH are coated with organic materials to improve their compatibility with the polymer. Coarser ground and air separated grades can be used in liquid resin compounding of thermosets for electrical applications, seats, panels and vehicle parts.
A number of other inorganic substances show flame retarding effects and are used in commercial applications. Most of them are used as synergists i.e. they enhance the performance of other flame retardants or they are used for specific effects like the suppression of smoke formation. For example, borates are used as mixtures of boric acids and borax as flame retardants for cellulose (cotton) and of zinc borate for PVC and other plastics like polyolefins, elastomers, polyamides, or epoxy resins. In halogen-containing systems, zinc borate is used in conjunction with antimony oxide, while in halogen-free systems it is normally used in conjunction with aluminium trihydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, or red phosphorus. In some particular applications zinc borate can be used alone. Boron containing compounds act by stepwise release of water and formation of a glassy coating which protects the surface.
Zinc compounds were initially developed as smoke suppressants for PVC (Zinc hydroxystannate). Later it was found that they also act as flame retardants in certain plastics mainly by promoting char formation.
Intumescent Flame Retardant systems expand to produce foams. They are used as coatings not only to protect combustible materials such as wood and plastics, but also steel structures in buildings, because steel loses its strength when exposed to high temperatures in a fire. The intumescent effect is achieved by combining an acid source like ammonium polyphosphate, a source of carbon, compounds which release noncombustible gases for blowing the foam on thermal decomposition and resin binders to stabilise the foam.
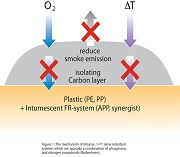
Expandable graphite is manufactured from flake graphite by treatment with strong acids like sulphuric or nitric acid. The acid is trapped in the crystal layers of the graphite ("intercalated"). When it is heated, the graphite starts to expand up to several hundred cm3 per gram, forming a protective layer for the polymer. Expandable graphite is used in plastics, rubbers (elastomers), coatings, textiles and especially in polymeric foams. To achieve an optimum flame retarding effect, the use of synergists like ammonium polyphosphate or zinc borate is often necessary. The black colour of graphite limits its applicability in some cases.
Nanocomposites have been gaining increasing attention since the late 1990s as potential new flame retardants. Nanocomposites
are polymer layered silicates based on aluminosilicate clay minerals like montmorillonite, composed of layers with gaps (gallery spaces) in between. These silicates have the ability to incorporate polymers. Research with nanocomposites has focused on plastics like polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyamides. Nanocomposites particularly prevent dripping and promote char formation. Therefore, they have been used as synergists in some polymer / flame retardant combinations. However, they require special processing and for the time being are not considered to become viable stand-alone flame retardants.
Other inorganic fillers like talcum or chalk (calcium carbonate) are sometimes denoted as flame retardants, but they do not specifically interact with the ignition process. On the contrary, simply by diluting the combustible polymer they reduce its flammability and fire load.
Inorganic Flame Retardant Additives, Inorganic Flame Retardant Polymers, Inorganic Flame Retardant Chemicals,Ammonium Polyphosphate
Shandong Novista Chemicals Co.,Ltd (Novista Group) , http://www.novistachem.com