 Source: China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association Recycling Metals Branch Among the major nonferrous metals, China's zinc recycling industry is relatively backward. At present, zinc (including zinc metals and compounds), which is consumed annually in the world, accounts for 70% and 30% of primary zinc and regenerated zinc, respectively. In China, more than 60% of zinc is used for steel anti-corrosion every year, and the recycling period is long. Therefore, the output of recycled zinc is only over 100,000 tons, accounting for about 3% of consumption. Although the regenerative zinc industry has attracted great attention in the industry, its gap with the world level cannot be ignored. Figure 2 Proportion of domestically produced recycled non-ferrous metals in total metal production
Source: China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association Recycling Metals Branch Among the major nonferrous metals, China's zinc recycling industry is relatively backward. At present, zinc (including zinc metals and compounds), which is consumed annually in the world, accounts for 70% and 30% of primary zinc and regenerated zinc, respectively. In China, more than 60% of zinc is used for steel anti-corrosion every year, and the recycling period is long. Therefore, the output of recycled zinc is only over 100,000 tons, accounting for about 3% of consumption. Although the regenerative zinc industry has attracted great attention in the industry, its gap with the world level cannot be ignored. Figure 2 Proportion of domestically produced recycled non-ferrous metals in total metal production 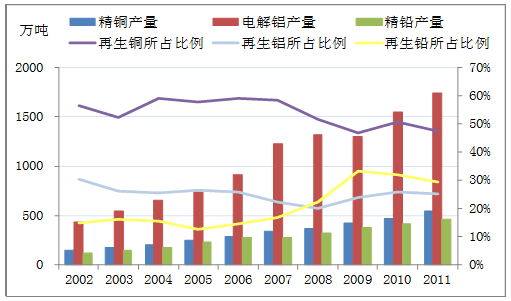 Source: China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association Recycling Metals Branch, Wind Although the output of recycled non-ferrous metals has increased year by year, the proportion of total metal output has varied. During the period 2002-2011, the proportion of recycled lead in refined lead production increased significantly. The proportion of recycled aluminum in electrolytic aluminum production was basically the same, while the proportion of recycled copper in refined copper production decreased. This is mainly because lead is an important raw material for the manufacture of automobile batteries, and the normal service life of a battery is generally about two years. Coupled with the rapid development of the domestic automobile industry in the past five years, the recycling process is faster than copper and aluminum. In 2011, the output of recycled copper, recycled aluminum and recycled lead accounted for 47.41%, 25.21% and 29.32% of the total metal output, respectively. Among them, copper was the highest proportion of regeneration, and the proportion of mainly recycled non-ferrous metals accounted for the corresponding total metal output. 33.27% fell to 30.32%. Overall, the proportion of recycled non-ferrous metals in total production has decreased, and there is still a big gap between the development of recycled metal industry in developed countries. This aspect is related to the total production of non-ferrous metals that China has rapidly increased to meet the needs of domestic economic development. On the other hand, it also shows that China's renewable non-ferrous metals industry still has a lot of room for development. II. Problems in China's Recycling Nonferrous Metals Industry First, China's recycled non-ferrous metals industry has a low concentration, and the entire industry is in a state of small, chaotic and scattered. In the past ten years, due to the better production efficiency of recycled non-ferrous metals, the process is not complicated. Many small enterprises have sprung up, the low-level repeated construction is serious, and the “three wastes†of small enterprises are not perfect, which is harmful to the surrounding environment. At present, there are more than 5,000 recycled metal enterprises, but only 1-2% of large and medium-sized backbone enterprises. Although a number of leading enterprises have emerged in the industry, a number of processing parks for the dismantling and smelting of recycled non-ferrous metals have been built, but the whole The strength is not strong, it is difficult to develop into an internationally competitive renewable non-ferrous metal enterprise group. Therefore, the task of increasing the degree of intensification and accelerating industrial upgrading is still quite arduous. Secondly, the level of technical equipment in China's recycled metal industry is not high, and the metal recovery rate is low. This is caused by two factors: On the one hand, the pretreatment industries such as dismantling, sorting and collecting waste metal in China are labor-intensive industries with low mechanization and automation. Most enterprises and self-employed households have poor equipment. Technology is backward and energy consumption is high; on the other hand, a variety of metal varieties are mixed, resulting in unstable product quality and difficulty in producing high quality products. Such as recycled copper, if the waste copper resources can be fully and rationally utilized, the recovery rate can reach 70-90%, while the recovery rate of copper metal in most domestic recycled copper plants is less than 50%. Third, rely too much on imported scrap metal resources. As a strategic resource, scrap metal has received universal attention from all countries. Under the circumstance of China's demand for scrap metal, major suppliers have introduced measures to restrict the export of scrap metal, so that the price of international scrap metal is rising rapidly. Increased the cost of China's scrap metal imports. III. Development trend of non-ferrous metals during the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†In view of the development status of recycled non-ferrous metals in China, the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Finance, and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and other seven ministries jointly issued Document No. 116 to refine China’s waste resources. The five-planning strategy is to eliminate backward production capacity, strengthen industry access, reduce the number of enterprises, encourage mergers and acquisitions, foster leading enterprises, and strengthen industrial concentration. It is estimated that by 2015, the top 10 enterprises in various industries will have an industrial concentration of more than 50%. The recycled copper and recycled aluminum industries will form a batch of large-scale enterprises with an annual output of more than 100,000 tons. The recycled lead industry will form a batch of 50,000 tons per year. The above scale enterprises. At the same time, it has formed a number of key areas for industrial agglomeration development, and its production capacity has exceeded 80%. Among them, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Shandong, Tianjin, Jiangxi and other regions as key support areas for recycled copper, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Chongqing, Shanghai, Henan and other regions as key development areas for recycled aluminum, and will increase Anhui, Henan, Shandong, Jiangsu, Hubei and other regions to develop the support of renewable lead. By then, the overall technical equipment level of the non-ferrous industry will also be significantly improved. Recently, the "12th Five-Year Plan for Energy Conservation and Environmental Protection Industry Development" issued by the State Council clearly stated that by 2015, 25 million tons of resources will be recycled, including 2 million tons of recycled copper and 2.5 million tons of recycled aluminum. It is estimated that by 2015, China's main recycled non-ferrous metal production will reach 12 million tons, and the proportion of recycled copper, recycled aluminum and recycled lead in the year's copper, aluminum and lead production will reach 40%, 30% and 40% respectively. In 2011, the main recycled non-ferrous metals were 8.35 million tons, of which recycled copper, recycled aluminum and recycled lead accounted for 47%, 25%, and 29% of copper, aluminum, and lead production, respectively. There is huge room for development. Chart 3 Domestic and non-ferrous metals production and proportion in 2011 and 2015
Source: China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association Recycling Metals Branch, Wind Although the output of recycled non-ferrous metals has increased year by year, the proportion of total metal output has varied. During the period 2002-2011, the proportion of recycled lead in refined lead production increased significantly. The proportion of recycled aluminum in electrolytic aluminum production was basically the same, while the proportion of recycled copper in refined copper production decreased. This is mainly because lead is an important raw material for the manufacture of automobile batteries, and the normal service life of a battery is generally about two years. Coupled with the rapid development of the domestic automobile industry in the past five years, the recycling process is faster than copper and aluminum. In 2011, the output of recycled copper, recycled aluminum and recycled lead accounted for 47.41%, 25.21% and 29.32% of the total metal output, respectively. Among them, copper was the highest proportion of regeneration, and the proportion of mainly recycled non-ferrous metals accounted for the corresponding total metal output. 33.27% fell to 30.32%. Overall, the proportion of recycled non-ferrous metals in total production has decreased, and there is still a big gap between the development of recycled metal industry in developed countries. This aspect is related to the total production of non-ferrous metals that China has rapidly increased to meet the needs of domestic economic development. On the other hand, it also shows that China's renewable non-ferrous metals industry still has a lot of room for development. II. Problems in China's Recycling Nonferrous Metals Industry First, China's recycled non-ferrous metals industry has a low concentration, and the entire industry is in a state of small, chaotic and scattered. In the past ten years, due to the better production efficiency of recycled non-ferrous metals, the process is not complicated. Many small enterprises have sprung up, the low-level repeated construction is serious, and the “three wastes†of small enterprises are not perfect, which is harmful to the surrounding environment. At present, there are more than 5,000 recycled metal enterprises, but only 1-2% of large and medium-sized backbone enterprises. Although a number of leading enterprises have emerged in the industry, a number of processing parks for the dismantling and smelting of recycled non-ferrous metals have been built, but the whole The strength is not strong, it is difficult to develop into an internationally competitive renewable non-ferrous metal enterprise group. Therefore, the task of increasing the degree of intensification and accelerating industrial upgrading is still quite arduous. Secondly, the level of technical equipment in China's recycled metal industry is not high, and the metal recovery rate is low. This is caused by two factors: On the one hand, the pretreatment industries such as dismantling, sorting and collecting waste metal in China are labor-intensive industries with low mechanization and automation. Most enterprises and self-employed households have poor equipment. Technology is backward and energy consumption is high; on the other hand, a variety of metal varieties are mixed, resulting in unstable product quality and difficulty in producing high quality products. Such as recycled copper, if the waste copper resources can be fully and rationally utilized, the recovery rate can reach 70-90%, while the recovery rate of copper metal in most domestic recycled copper plants is less than 50%. Third, rely too much on imported scrap metal resources. As a strategic resource, scrap metal has received universal attention from all countries. Under the circumstance of China's demand for scrap metal, major suppliers have introduced measures to restrict the export of scrap metal, so that the price of international scrap metal is rising rapidly. Increased the cost of China's scrap metal imports. III. Development trend of non-ferrous metals during the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†In view of the development status of recycled non-ferrous metals in China, the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Finance, and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and other seven ministries jointly issued Document No. 116 to refine China’s waste resources. The five-planning strategy is to eliminate backward production capacity, strengthen industry access, reduce the number of enterprises, encourage mergers and acquisitions, foster leading enterprises, and strengthen industrial concentration. It is estimated that by 2015, the top 10 enterprises in various industries will have an industrial concentration of more than 50%. The recycled copper and recycled aluminum industries will form a batch of large-scale enterprises with an annual output of more than 100,000 tons. The recycled lead industry will form a batch of 50,000 tons per year. The above scale enterprises. At the same time, it has formed a number of key areas for industrial agglomeration development, and its production capacity has exceeded 80%. Among them, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Shandong, Tianjin, Jiangxi and other regions as key support areas for recycled copper, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Chongqing, Shanghai, Henan and other regions as key development areas for recycled aluminum, and will increase Anhui, Henan, Shandong, Jiangsu, Hubei and other regions to develop the support of renewable lead. By then, the overall technical equipment level of the non-ferrous industry will also be significantly improved. Recently, the "12th Five-Year Plan for Energy Conservation and Environmental Protection Industry Development" issued by the State Council clearly stated that by 2015, 25 million tons of resources will be recycled, including 2 million tons of recycled copper and 2.5 million tons of recycled aluminum. It is estimated that by 2015, China's main recycled non-ferrous metal production will reach 12 million tons, and the proportion of recycled copper, recycled aluminum and recycled lead in the year's copper, aluminum and lead production will reach 40%, 30% and 40% respectively. In 2011, the main recycled non-ferrous metals were 8.35 million tons, of which recycled copper, recycled aluminum and recycled lead accounted for 47%, 25%, and 29% of copper, aluminum, and lead production, respectively. There is huge room for development. Chart 3 Domestic and non-ferrous metals production and proportion in 2011 and 2015  Source: MRI
Source: MRIZirconia Ceramic Rod-plunger main features: high strength, high fracture toughness, high hardness and high density, stability, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.
Zirconia Ceramic Rods - plunger applications: ultra-fine grinding equipment, fine chemicals, electronic pastes, semiconductors, new energy, nano-new materials, medical equipment, precision casting, structural ceramics, refractory materials, electronic communications, sensitive ceramics, petroleum Chemical, aerospace, mechanical manufacturing, fiber optic connectors, battery materials and other high-end fields.
Alumina Ceramic Rod,Alumina Ceramic Roller,Polished Alumina Ceramic,Alumina Insulation Ceramic Rod
SHENZHEN HARD PRECISION CERAMIC CO.,LTD , http://www.hardcm.com