Recently, the State Key Laboratory of Information and Functional Materials, Shanghai Institute of Microsystems and Information Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences has made progress in research on high mobility graphene single crystal wafers. Related research results are based on Wafer-scale growth of single-crystal graphene on vicinal The topic of Ge(001) substrate was published on Nano Today.
Single-crystal graphene is considered to be one of the most potential channel materials in the post-silicon CMOS era due to its ultra-high carrier mobility. The single-crystal graphene wafer prepared directly from a CMOS technology-compatible substrate is graphite The basis for ene's move towards microelectronics applications is still challenging. The mainstream CMOS technology in the industry is based on (001) crystal silicon wafers, which means that compared with (110) crystal germanium wafers, (001) crystal germanium wafers are more compatible with CMOS processes. However, generally, the orientation of graphene crystal domains grown on (001) crystal plane germanium cannot be controlled, and the graphene wafers formed by combining the crystal domains contain a large number of grain boundaries, and graphene single crystal waferene cannot be obtained, which affects graphene in microelectronics. Potential applications in the field.
The study found that single-oriented graphene crystal domains can be obtained by using (001) crystal plane germanium with a bevel angle of more than 10° as the graphene growth substrate. By seamlessly splicing these graphene crystal domains with the same orientation, the researchers prepared high mobility single crystal graphene wafers on the germanium substrate surface with a 15° cut angle (001) crystal plane. Experimental results and theoretical calculations show that the nucleation orientation of the graphene domain is closely related to the bevel angle of the germanium substrate. At the same time, the researchers used atomic force microscopy to continuously observe the growth behavior of graphene. The results showed that the nucleation of graphene along the oblique cutting direction on the germanium substrate surface with a 15° cut angle (001) crystal plane was suppressed, and was perpendicular to The graphene nucleation in the chamfer direction is not affected. During the entire graphene growth process, no new graphene nucleation occurs, and the preparation of single-crystal graphene wafers is made by seamless splicing of graphene crystal domains with the same orientation. The single-crystal graphene wafers prepared by this technology exhibit ultra-high carrier mobility, which is expected to provide material support for the development of graphene nanoelectronic devices.
The thesis was completed in cooperation with the State Key Laboratory of Information and Functional Materials by Shanghai Microsystems Institute and East China Normal University. Li Panlin, a direct student of Shanghai Institute of Microsystems, and Wei Wenya, a doctoral student of East China Normal University, are co-first authors. Di Zengfeng, a researcher of Shanghai Institute of Microsystems and Yuan Qinghong, a professor of East China Normal University, are co-corresponding authors. Shanghai Institute of Microsystems is the first completion unit . The research work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project, the Chinese Academy of Sciences Frontier Science Key Research Project, the National Natural Science Foundation Outstanding Youth Fund, the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Strategic Leading Science and Technology Project.
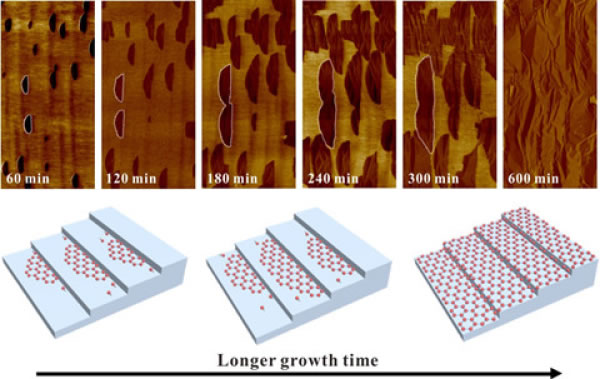
Continuous observation of the growth process of single crystal graphene by atomic force microscope
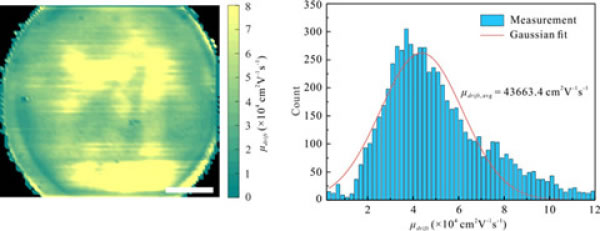
Distribution and statistics of carrier mobility in 4 inch single crystal graphene wafers
Polyquaternium-22 PQ-22 CAS 53694-17-0
Pq-22 Used In Cosmetic Industry,Polyquaternium-11 Pq-11 In Cosmetic,Dadmac And Acrylic Acid Copolymer,Pq-22 Cas No 53694-17-0
ZHEJIANG XINHAITIAN BIO-TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD. , https://www.dadmacxht.com