October 15, 2019
How is the car built step by step?
Abstract Regarding the production line of automobiles, let us first look at a flow chart of automobile production: Let's talk about the specific aspects: First, use the punch to press the steel plate into the outer shell of the car. This is a very important step in automobile manufacturing. It involves the linear design and mode of the car...
Regarding the production line of the car, let us first look at a car production flow chart: 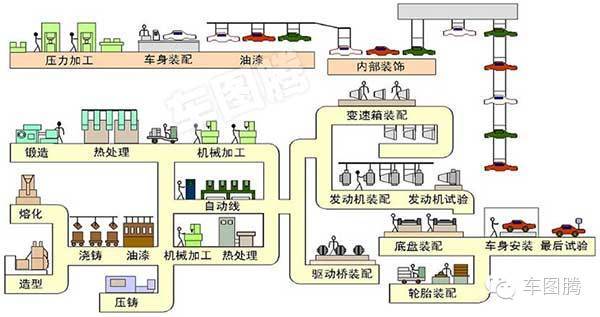
Let's talk about the specific aspects:
First, the press is used to press the steel plate into the outer casing of the car. This is a very important step in the automobile manufacturing. It involves the linear design of the car and the stamping design of the mold. If the parent factory cannot complete this step independently, it means that The production technology of the factory has not yet reached the required standard, and at best it is just an assembly plant.
2. After the car shell is completed, in order to facilitate the welding work in the subsequent steps, the car body is usually reversed.
3. After the initial welding is completed, the car body is righted up and the door and hood are added.
Fourth, then try to remove the burrs and ciphers of each steel plate on the car shell, and pre-fabricate the chassis for the painting of the car body.
5. The above is the rough manufacturing process of the car body part. Then it is necessary to assemble the system of girders, shockproof, transmission and engine. These parts can be said to be the internal organs of the car, which is very important; especially the engine, but also the heart of the car.
6. If a country's auto industry cannot complete the design and manufacture of the engine completely independently, it means that the country's auto industry has not yet taken root. After the above-mentioned girders, shockproof, transmission, and engine devices are completed, the vehicle body can be hoisted from top to bottom to form a prototype of the automobile.
Seventh, the rest of the work is the interior decoration of the car, including glass, wipers, seat, etc., in addition to the radiator (water tank), hydraulic system, fuel system and wheels, etc., the whole car can be considered a success.
Eight, however, in order to ensure the car dealer's credit and the basic safety of consumers, a series of tests must be carried out before the car can be shipped.
These tests include roller test, leak test and road test. The main purpose of the test is to test the performance of the engine, transmission system, joystick, brakes, lighting and body leakage. After these tests, the car It can be shipped from the factory.
The following is a detailed description of the car's manufacturing process and process:
Casting
Casting is a method of producing a product by pouring molten metal into a cavity of a mold and cooling and solidifying. In the automobile manufacturing process, there are many parts made of cast iron, which account for about 10% of the total weight of the car, such as the cylinder block, the transmission case, the steering gear housing, the rear axle housing, the brake drum, various brackets, etc. . Cast iron parts are usually made of sand. The sand type raw material is mainly composed of sand and mixed with a binder, water, and the like. The sand material must have a certain bond strength in order to be molded into the desired shape and to withstand the scouring of high temperature molten iron without collapse. In order to mold a cavity in the sand mold that conforms to the shape of the casting, it is necessary to first make a model of wood, called a wood mold. The volume of the hot molten iron will be reduced after cooling. Therefore, the size of the wood mold needs to be increased according to the original size of the casting, and the surface to be machined is correspondingly thickened. Hollow castings require the formation of a sand core and a corresponding core wood mold (core box). With a wooden mold, you can convert the cavity sand type (casting is also called "turning sand"). When manufacturing the sand mold, it is necessary to consider how the upper and lower flasks are separated to take out the wood mold, and also consider where the molten iron flows from, and how to fill the cavity to obtain high quality castings. After the sand mold is made, it can be poured, that is, the molten iron is poured into the sand cavity. When pouring, the temperature of the molten iron is between 1250 and 1350 degrees, and the temperature is higher during melting.
2. forging
Forging processes are widely used in the automotive manufacturing process. Forging is divided into free forging and model forging. Free forging is a processing method in which a metal blank is placed on an anvil to withstand impact or pressure (called "ironing" in the workshop). The blanks of the car's gears and shafts are processed by free forging. Model forging is a processing method in which a metal blank is placed in a die of a forging die and subjected to impact or pressure. Model forging is a bit like the process of the dough being pressed into a biscuit shape in a mold. Compared with free forging, the shape of the workpiece produced by die forging is more complicated and the size is more precise. Typical examples of die forgings for automobiles are: engine connecting rods and crankshafts, automobile front axles, steering knuckles, and the like.
3. Cold stamping
Cold stamping or sheet stamping is a processing method in which a metal sheet is subjected to pressure in a die to be cut away or formed. Daily necessities, women's aluminum pans, lunch boxes, washbasins, etc. are made by cold stamping. For example, in the manufacture of a lunch box, it is first necessary to cut a rectangular shape and have four rounded blanks (known as "dropping" by the expert), and then press the blank into the concave mold with a punch to form it (the artist calls "draw"). ). In the drawing process, the flat sheet becomes a box shape, the four sides of which are vertically bent upward, and the materials of the four corners are piled up and wrinkles are seen. Automotive parts that are cold stamped are: engine oil sump, brake floor, car frame and most body parts. These parts are generally formed by blanking, punching, drawing, bending, flanging, trimming and the like. In order to manufacture cold stamped parts, a die must be prepared. The die is usually divided into two pieces, one of which is mounted on the press and can slide up and down, and the other is mounted under the press and fixed. At the time of production, the blank is placed between two dies, and when the upper and lower dies are closed, the stamping process is completed. The productivity of stamping is very high, and parts with complex shapes and high precision can be manufactured.
4. Welding
Welding is a processing method in which two pieces of metal are locally heated or simultaneously heated and pressurized to be joined together. The welding method in which the common worker holds the mask in one hand and the welding tongs and the welding rod connected to the electric wire in the other hand is called manual arc welding, which is a high-temperature melting electrode and a weldment generated by arc discharge to be joined. Manual arc welding is not widely used in automobile manufacturing. The most widely used in the manufacture of automobile bodies is spot welding. Spot welding is suitable for welding thin steel sheets. During operation, two electrodes are pressed against two steel sheets to be bonded together, and the bonding points (circles having a diameter of 5-6 )) are heated and melted to be firmly joined. When two body parts are welded, the edges of the two parts are welded every 50-100 ,, so that the two parts form a discontinuous multi-point connection. Welding the entire car body usually requires thousands of solder joints. The strength of the solder joints is very high. Each solder joint can withstand a pulling force of 5kN, and even the steel sheet is torn, and the solder joint portion cannot be separated. Gas welding, which is common in repair shops, is a method in which acetylene is burned and assisted by oxygen to generate a high-temperature flame to melt and join the electrode and the weldment. It is also possible to use this high temperature flame to cut the metal, called gas cutting. Gas welding and gas cutting applications are more flexible, but the heat affected zone of gas welding is larger, which causes deformation and metallographic structure changes of the weldment, and performance is degraded. Therefore, gas welding is rarely used in automobile manufacturing.
5. Metal cutting
Metal cutting is a process in which a metal blank is cut layer by layer with a cutter; the workpiece is obtained in the desired shape, size and surface roughness. Metal cutting includes both fitter and machining methods. The fitter is a processing method for workers to cut with hand tools. It is flexible and convenient to operate, and is widely used in assembly and repair. Machining is done by means of machine tools, including: turning, planing, milling, drilling and grinding.
1) Turning: Turning is the process of machining a workpiece with a turning tool on a lathe. The lathe is suitable for cutting a variety of rotating surfaces, such as inner and outer cylinders or conical surfaces, as well as turning end faces. Many of the axle parts and gear blanks of the car are machined on a lathe.
2) Planing: Planing is the process of machining a workpiece with a planer in a planer. Planers are suitable for processing horizontal, vertical, beveled and grooved surfaces. The cylinder block and the cylinder head on the car, the matching plane of the transmission case and the cover are all processed by a planer.
3) Milling: Milling is the process of machining a workpiece with a milling cutter on a milling machine. Milling machines can process bevels, grooves, and even old milling such as machined gears and curved surfaces for a wide range of automotive parts. The molds for cold stamping of automobile bodies are all milled. The computer-controlled CNC milling machine can process workpieces with complex shapes and is the main machine tool for modern machining.
4) Drilling and boring: Drilling and boring are the main cutting methods for machining holes.
5) Grinding: Grinding is the process of machining a workpiece with a grinding wheel on a grinding machine. Grinding is a finishing method that produces workpieces with high precision and roughness and that can grind workpieces with very high hardness. Some heat-treated automotive parts are finished with a grinding machine.
6. Heat treatment
Heat treatment is a method of reheating, holding or cooling solid steel to change its structure to meet the requirements of the parts or the process requirements. The temperature of the heating, the length of the holding time, and the speed of the cooling can cause different structural changes in the steel. The blacksmith immerses the heated steel in water for rapid cooling (known as quenching by the expert), which increases the hardness of the steel, which is an example of heat treatment. The heat treatment process includes annealing, normalizing, quenching, and tempering. Annealing is to heat the steel piece for a certain period of time, and then slowly cool it together with the furnace to obtain a finer and uniform structure and reduce the hardness to facilitate the cutting process. The normalizing heat is to heat the steel piece, take it out of the furnace after being kept warm, and then cool it in the air, which is suitable for refining the low carbon steel. Quenching is the heating of steel, which is quickly cooled in water or in oil to increase hardness. Tempering is usually a subsequent step of quenching. The quenched steel is reheated, cooled and then cooled to stabilize the structure and eliminate brittleness. There are many automotive parts, not only to preserve the toughness of the core, but also to change the surface structure to improve the hardness, it is necessary to use surface heat treatment such as high-frequency quenching or carburizing, cyanidation.
7. assembly
Assembly is to connect and combine various parts into parts by connecting parts (bolts, nuts, pins or snaps, etc.) according to certain requirements, and then connect and combine the various parts into a complete vehicle. Whether the parts are combined into parts or the parts are assembled into a complete vehicle, the interactions specified in the design drawings must be met to achieve the intended performance of the part or the vehicle. For example, when assembling a transmission to a clutch housing, the centerline of the transmission input shaft must be aligned with the centerline of the engine crankshaft. This way of centering is not regulated by the assembly worker (fitters) during assembly, but by design and manufacturing. If you visit a car manufacturer, the most attractive is the car assembly line. On this assembly line, drive a car every few minutes. Take the general assembly line of China's FAW Jiefang brand truck as an example. This assembly line is a 165m long conveyor chain. The car moves to the various stations along the conveyor chain and is gradually assembled. There are also conveyor chains around the engine assembly, cab assembly, wheel assembly, etc. Each workshop is transported to the corresponding station on the main assembly line. First place the frame at the beginning of the conveyor chain (bottom-to-day), then mount the rear axle assembly (including leaf springs and hubs) and front axle assembly (including leaf springs, steering knuckles and hubs) to the frame Then, turn the frame over to install the steering gear, air reservoir and brake lines, fuel tank and tubing, wires and wheels, etc. Finally install the engine assembly (including the clutch, transmission and central brake), connect the drive shaft, and then Install the cab and front panel parts. At this point, the car can drive off the assembly line.
50-80Mm Calcium Carbide,High Purity Cac2 Calcium Carbide,Inorganic Salt Calcium Carbide Stone,Calcium Carbide For Gas Evolution
shizuishan pengsheng chemical co.,ltd , https://www.szspschem.com